Off-policy Actor Critic
Introduction
- Policy gradient is on-policy, because the gradient
- We can convert it to off-policy by using importance sampling.
Illustrative Example
Consider a random variable . If the probability distribution of is :
then the expectation of is
Question: how to estimate by using some samples ?
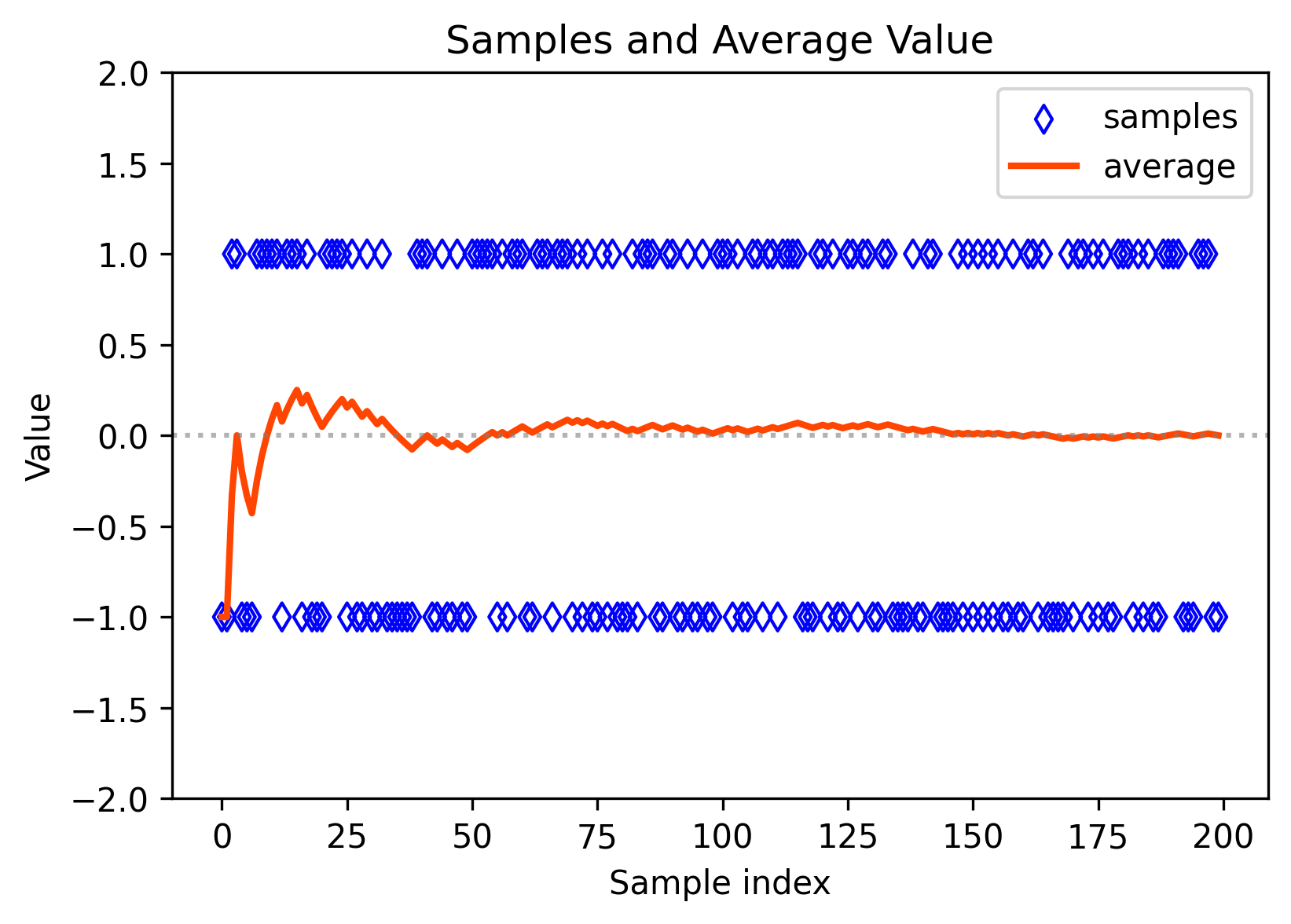
Case 1 (familiar)
The samples are generated according to :
Then, the average value can converge to the expectation:
More
- See the law of large numbers.
- code: Figure Samples Average
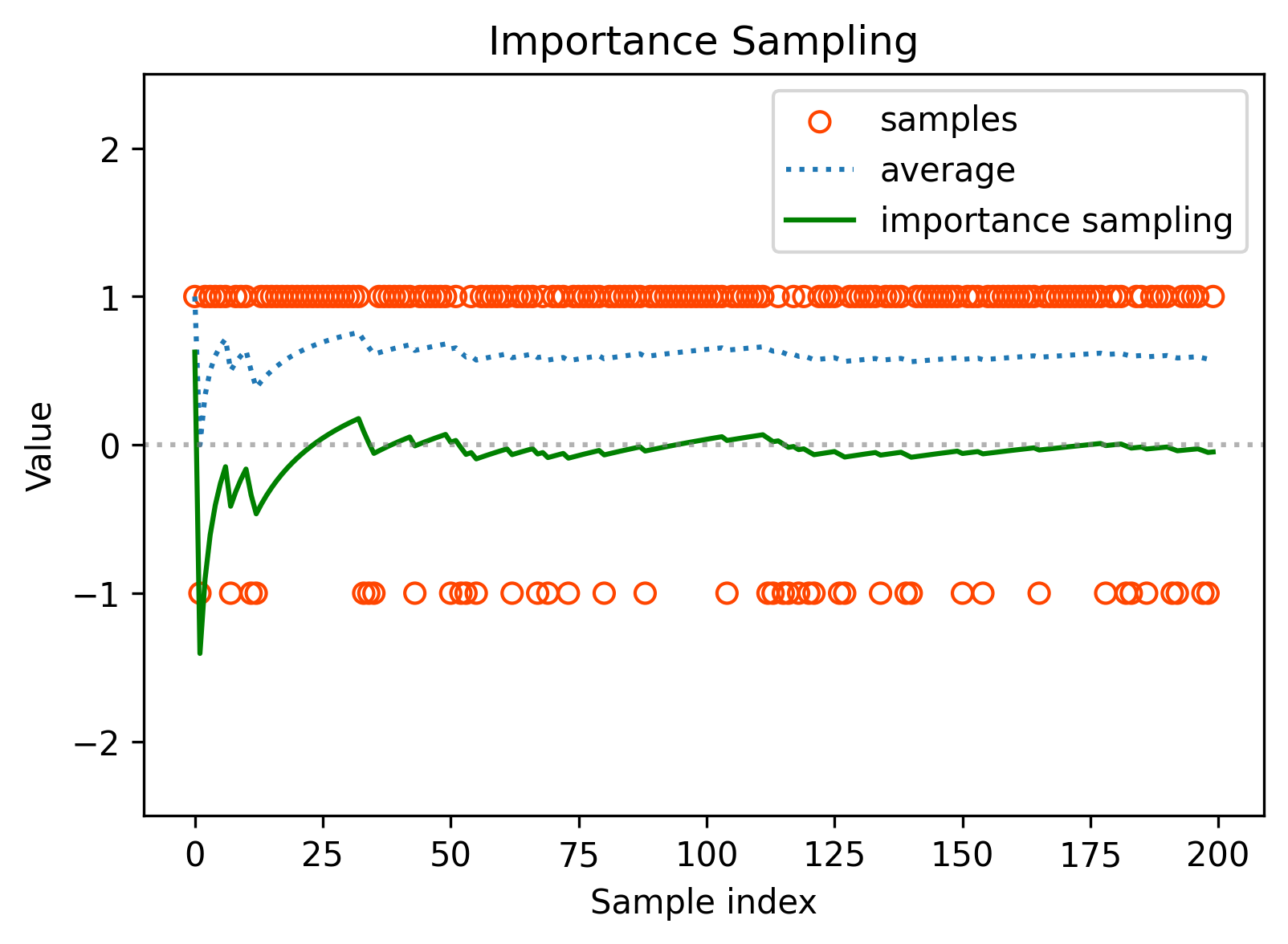
Case 2 (new)
The samples are generated according to another distribution :
The expectation is
If we use the average of the samples, then without suprising
Can we use to estimate ?
- Why to do that? We want to estimate where is the target policy based on the sample of a behavior policy .(off-policy: get , want )
- How to do that? We can’t directly using above, we need to re-weight the samples by the ratio of the target policy and the behavior policy, see Importance sampling.
Importance sampling
Note that
Then we can estimate by estimating .
How to estimate ? Easy. Let
Therefore, is a good approximation for .
- If , the importance weight is one and becomes .
- If , can be more often sampled by than . The importance weight can emphasize the importance of this sample, vice versa.
你可能会问:如果都知道 和了,为什么不直接计算的期望呢(还搁这计算)?
- 当x是离散的时候:需要注意的是,我们有时候是获得不了all x的,只能一个一个采样获得x(或者从replay buffer里面采样一个batch),我们可以用到重要性采样了来更新我们整体的期望。
- 当x是连续时:比如下一节AC DPG就开始介绍连续action应该怎么做,此时我们要做整个action space空间上的动作概率()积分是非常困难的,但是如果只是获取某一个特定动作的概率就简单不少(TD,determinisitic),此时我们就可以用重要性采样来对当前的梯度进行修正(),更多连续的细节可以参考Sutton书中的13.7节。
TL;DR
一句话总结
当我们用一个分布的样本去估计另一个分布的期望时,我们需要用和的比值作为权重来调整样本的平均值。就element-wise的角度而言,我们就是拿将第i个样本除以再乘以就可以了。
If , then
Theorem of off-policy policy gradient
- Suppose is the behavior policy that generates experience samples.
- Our goal is to use these samples to update the target policy that can optimize the metric where is the stationary distribution under policy .
In the discounted case where , the gradient of is
where is the behavior policy and is the state distribution.
我们这里的和之前所提及的on-policy distribution 做了区分,这里是off-policy的
Algorithm of off-policy actor-critic
The corresponding stochastic gradient-ascent algorithm is
Similar to the on-policy case,
Then, the algorithm becomes
Implementation
Compared with Implementation
Later
discrete action space ⇒ continuous action space
Appendix
Figure Samples Average
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generate random values +1 or -1, with probability 0.5 for each
np.random.seed(1337) # Set random seed to ensure reproducibility
num_samples = 200
samples = np.random.choice([1, -1], size=num_samples)
# Calculate the average
# cumulative_avg = np.cumsum(samples) / np.arange(1, num_samples + 1)
cumulative_avg = np.zeros(num_samples)
mean = 0 # Initial mean
for k in range(1, num_samples + 1):
mean = mean - (1 / k) * (mean - samples[k - 1])
cumulative_avg[k - 1] = mean
# Create plot
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.scatter(range(num_samples), samples, marker='d', facecolors='none', edgecolors='blue', label="samples")
plt.plot(range(num_samples), cumulative_avg, color='orangered', label="average", linewidth=2)
# Turn off grid
plt.grid(False)
# Add a gray dashed line at Value = 0
plt.axhline(y=0, color='gray', linestyle=':', alpha=0.6)
# Set legend and labels
plt.xlabel("Sample index")
plt.ylabel("Value")
plt.legend()
plt.ylim(-2, 2)
plt.title("Samples and Average Value")
# plt.show()
plt.savefig("Figure_Samples_Average.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')Figure Importance Sampling
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generate random values +1 or -1, with probability 0.5 for each
np.random.seed(42) # Set random seed to ensure reproducibility
num_samples = 200
samples = np.random.choice([1, -1], size=num_samples, p=[0.8, 0.2])
# Calculate the average
avg = np.zeros(num_samples)
mean = 0 # Initial mean
for i, sample in enumerate(samples):
alpha = 1 / (i + 1)
mean = mean - alpha * (mean - sample)
avg[i] = mean
# Importance sampling
# Calculate the average using importance sampling
avg_imp = np.zeros(num_samples)
mean_imp = 0 # Initial mean
for i, sample in enumerate(samples):
alpha = 1 / (i + 1)
# Update the mean using importance sampling
ratio = 0.5 / (0.8 if sample == 1 else 0.2)
mean_imp = mean_imp - alpha * (mean_imp - sample) * ratio
avg_imp[i] = mean_imp
# Create plot
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.scatter(range(num_samples), samples, marker='o', facecolors='none', edgecolors='orangered', label="samples")
plt.plot(range(num_samples), avg, label="average", linestyle=':')
plt.plot(range(num_samples), avg_imp, label="importance sampling", color='green')
# Turn off grid
plt.grid(False)
# Add a gray dashed line at Value = 0
plt.axhline(y=0, color='gray', linestyle=':', alpha=0.6)
# Set legend and labels
plt.xlabel("Sample index")
plt.ylabel("Value")
plt.legend()
plt.ylim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.title("Importance Sampling")
# plt.show()
plt.savefig("Figure_Importance_Sampling.png", dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')